Method Comparison
What are the differences between Umny ground property predictions and the other ways to get ground temperature and thermal conductivity?

Umny ML model captures more of nature's complexity than we can fit in equations.
Analytical Equations
X Averages out complexity
Х Limited by few variables and low dimensionality
Х Must know accurate values for all equation inputs/variables
Umny ML Apps
✓ More like pattern recognition than interpolation
✓ Able to utilize algorithm complexity far beyond
what humans can manually understand or work with
✓ Can learn continuously from real-world data,
modeled data, and analytical methods
✓ Can generate accurate results with easy inputs
(ex: date, depth, location)
Many people use this equation to calculate ground temperature:
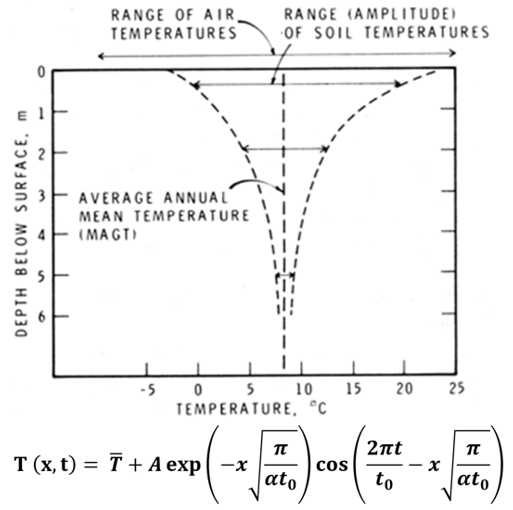
This equation requires accurate air temperature, and thermal diffusivity data for each location you’d like to test. Since thermal diffusivity cannot be measured directly, this value is most often assumed, which means the resulting temperature result is reliant on how well this value is assumed. In comparison, Umny AI predicts based on real-world measurements, no assumptions required, it is also much easier and faster to generate predictions with GTP than using this equation.
Using soil texture results from actual samples or estimated from tables, soil thermal conductivity is often calculated with the following equations:
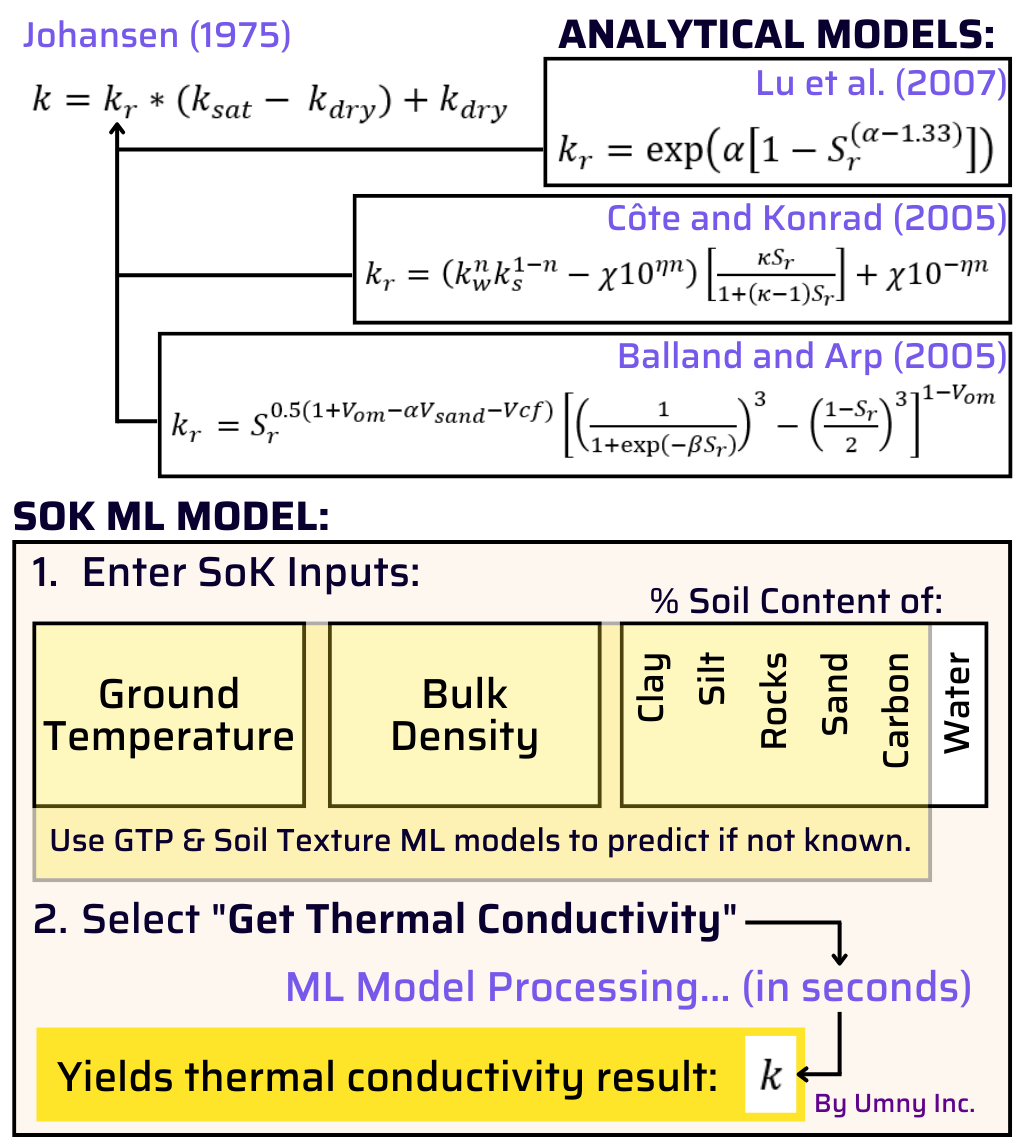
It is quickly obvious that our ground apps are easier to use, but they are also more accurate than these equations. When using the same values for soil texture and bulk density, Umny predictions were 32% more accurate at predicting the soil conductivity that was actually measured than the above equations.

Predicting what's below ground without having to dig, or wait.
Our ML can find most of the results of a physical test (ex: a Thermal Response Test, TRT), without needing to mobilize any equipment. It also works well with physical tests as a second opinion or to validate sensor measurements.
Physical Tests
X Time consuming and costly
Х Potential for test to interfere with results
Х Must be installed below ground to read deeper than the top surface
Х Post calculations must be done to determine properties (especially since there is no direct way to measure thermal conductivity)
Х Requires specialized personnel and equipment that may not be available widely, or at each project stage
Umny ML Apps
✓ Fast and inexpensive
✓ Fully remote, does not disturb the ground
✓ Predicts from the top surface to deeper depths with the same app
✓ No pre or post calculations required
✓ Usable by anyone with app access
✓ Shows seasonal variations, not just the results of the test day/time

Copyright © 2021 – 2023. Umny Inc. All rights reserved.